A Revised Edition
of the Beer Game *
Hironori Kurono, Kyushu International University,
Toshiro Shimada, Meiji Univ., Saburo Kameyama, Chuo Univ., Tomofumi
Sumita, The Univ. of Electronic-Communication, Shoji Hidaka, NTT
Data Co., Shin Ichikawa, The Univ. of Transportation Economics
[ABSTRACT]
This
paper shows a revised edition of the Beer Game: a revised board,
steps and record sheets. This edition is based on the original
Beer Game, which has been distributed by the System Dynamics Society,
and a revised one of Innovation Associates Ltd. The goal of this
edition is that participants of the game can experience more realistic
features of the Beer Game within one hour.
Basic Problems of the Beer
Game
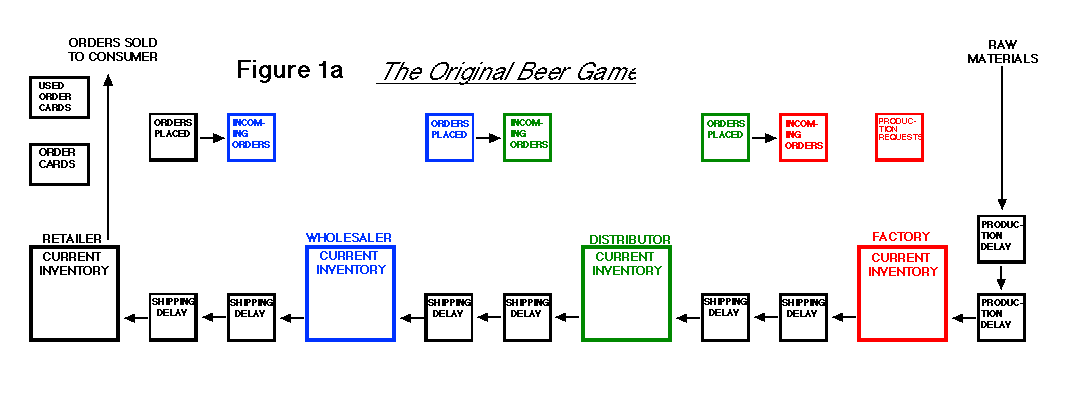
We are familiar with
the board of the original Beer Game that shows information flow
on the upper side and logistics on the lower side (Figure 1a).
While all the arrows are painted black, the board is designed
with four colors for four positions: black for a retailer, blue
for a wholesaler, green for a distributor, and red for a factory.
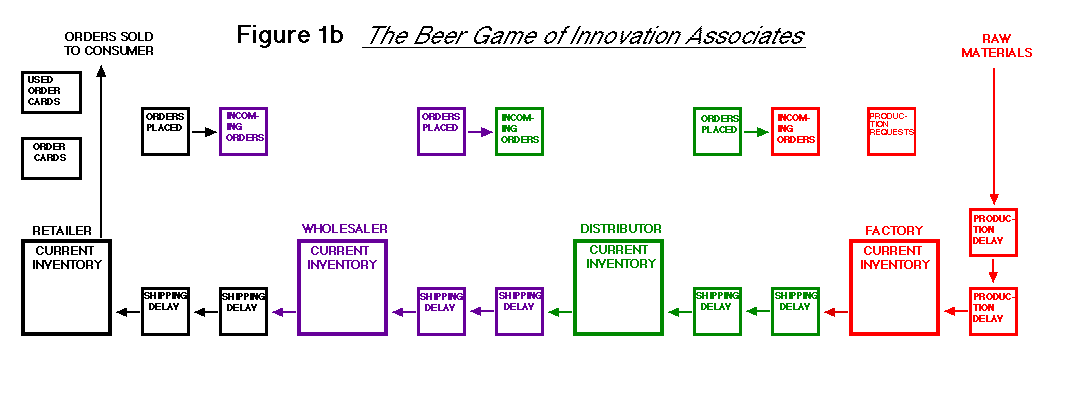
However, Innovation Associates Ltd. designed the board by coloring
these arrows differently: the color of the arrows at each position
is the same as the color for each position (Figure 1b).
Violet is used in the place of blue of the original game.
Coloring the board greatly helps a player
easily understand the role of his position and easily play the
game. One problem is that the roles of the positions on these
boards do not completely correspond to those in reality. For example,
while a real retailer checks and receives incoming products, he
does not transport them. He places orders, but dose not bring
them to a real wholesaler. These activities are usually executed
by a real wholesaler.
The steps of the original Beer Game are the
followings (Sterman):
| 1 . | Receive inventory and advance the shipping.
|
| Factory advance the production delay. |
| 2. | Look at incoming orders and fill orders.
|
| All incoming orders plus orders in backlog must be filled.
|
| If your inventory is insufficient to fill incoming orders plus backlog, fill as many orders as
|
| you can and add the remaining orders to your backlog.
|
| 3. | Record your inventory or backlog. |
| 4. | Advance the order slips. |
| Factories introduce production requests from last week into the production delay.
|
| 5. | Place and record your orders.
|
There are only five steps, which makes it
easy for the leader to give instructions to participants. Nonetheless,
each participant is often confused with what to do when a leader
calls out each step because each step basically treats all the
roles of the four positions at a time. As a result, this causes
a participant to make mistakes: moving an incorrect part or recording
an incorrect value, sometimes forgetting to do a step. So a leader
needs assistants who can quickly correct mistakes of a participant
and instruct him on what to do from the opposite side of the board.
The original game uses only one record sheet
with three columns: Inventory, Backlog and Order. The record sheet
of Innovation Associates Ltd. is very similar to the original,
except for an equation pasted at each row of the record sheet
so that a participant can compute inventory or backlog correctly
according to this equation. This equation, however, is complicated
for a student who has not experienced computing backlogs in business.
In both record sheets, it takes time for
everyone to compute when a backlog happens in the game. What makes
things more confused is that a backlog is positive when recorded
on the record sheet, and negative when it is mapped on a graph
sheet at the debriefing stage. This is due to two equations used
in these record sheets. If a positive value is treated as inventory
and a negative value is treated as backlog, only one equation
is enough. Thus, if a player can compute inventory or backlog
just by following the operator in each cell on the record sheet,
speed and accuracy of the game will be much improved.
Integrating the board, the steps
and the record sheets
To overcome these
basic problems, a revised board, steps and record sheets need
to be redesigned.
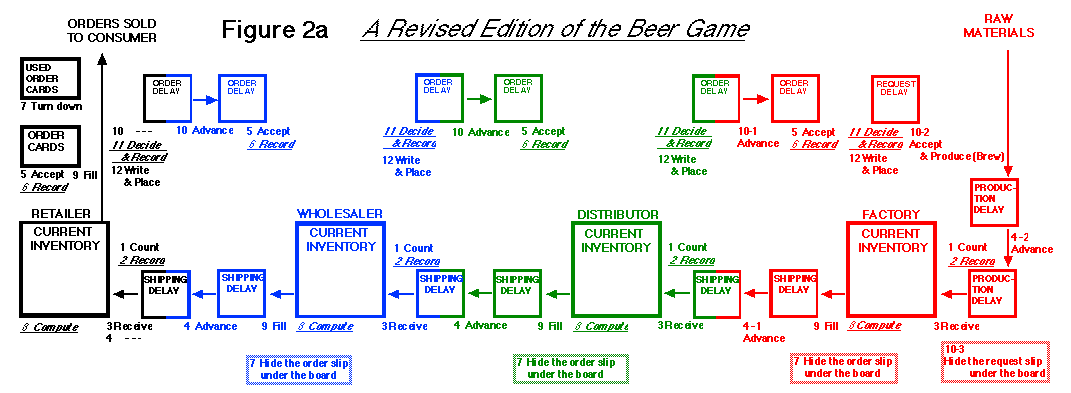
In this revised board (Figure 2a),
all the names of the upper boxes include "DELAY" because
they are actually delays: order delays and the production request
delay. Second, the number and short words of each step are shown
close to an appropriate box for the step so that a player can
notice and execute the step at once. Italic steps indicate that
they are executed on a record sheet. Third, coloring clearly separates
all the positions into four color areas including arrows. For
example, the Òshipping delayÓ box at the left of
the bottom is divided into two parts by coloring black and blue
because a wholesaler (Blue) advances goods into this box, while
a retailer (Black) counts incomoing products in this box and recieves
them into his inventory box.
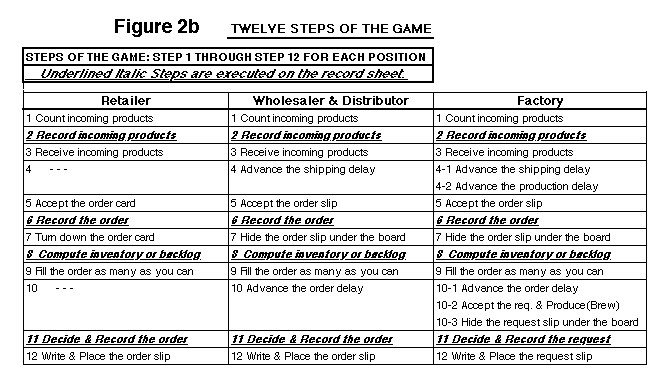
There are new twelve steps for each position
(Figure 2b)
. A game leader calls out each
step so participants know the main and specific roles of the four
positions. As it is convenient for a player to have a specific
record sheet of each position, four kinds of revised record sheets
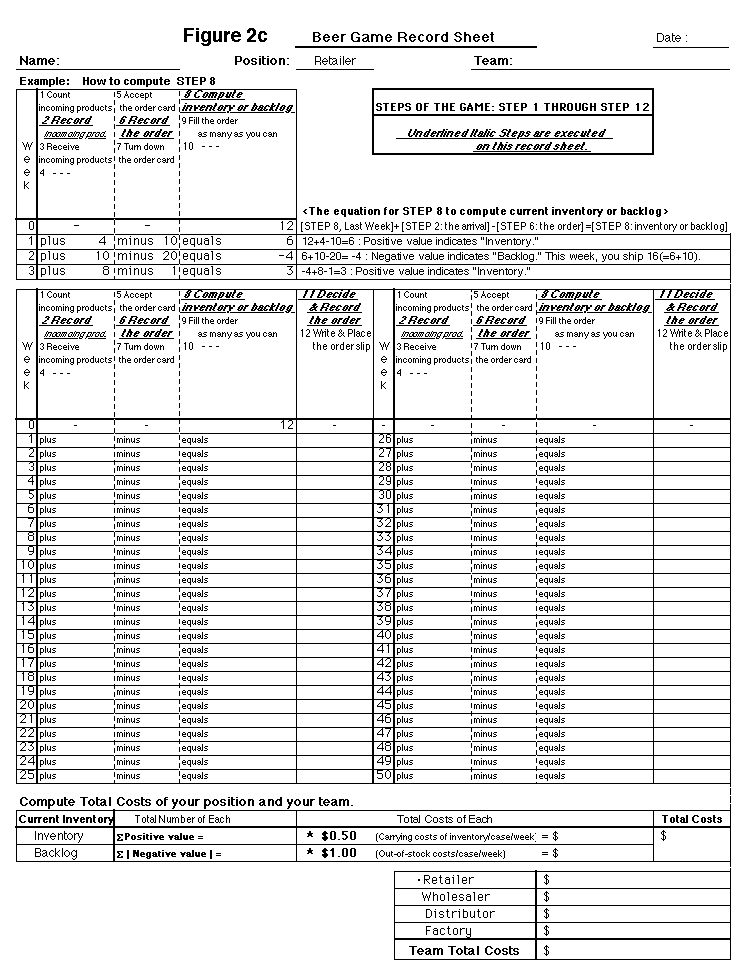
are prepared (Figure 2c).
In the table of this record sheet, two columns
are added to the original version: ÒRecording incomoing
productsÓ and ÒRecording the order.Ó Also,
two columns of the original record sheet, ÒInventoryÓ
and ÒBacklogÓ are unified into one column: ÒCompute
Inventory or BacklogÓ while the other one is ÒDecide
& Record the order.Ó As a result, there are four columns
in the table and these columns on the record sheet are in the
order of the equation. The equation, which is explained using
an example at the top of the record sheet (how to compute inventory
or backlog), helps a player to become immediately familiar with
computing inventory or backlog easily by following an operator
inside a cell. At the end of the game, when a backlog is negative,
the absolute value of each negative value of a backlog is added
up for total costs. The other two columns, Date and Name, are
added at the top of this record sheet. The Name column is also
necessary on the graph sheet in order to utilize the graph at
the debriefing stage.
In this way, the board, the steps and the
record sheets are integrated in this revised edition of the Beer
Game by redesigning the equation and roles for each participant.
*
We had valuable suggestions from Shogo Sakakura, Takayuki Toyama
and Koichi Yamauchi, who joined playing the Beer Game at the office
of the Japanese Chapter of the System Dynamics Society on Dec.
21, 1996.
References
John Sterman 1984 "Instructions for Running the Beer Distribution"
D-3679 System Dynamics Group, Sloan School of Management, Massachusetts
Institute of Technology
ISDC '97 CD Sponsor 

