INTRODUCTION
For its own nature, universities have an unavoidable vocation of academic and scientific excellence, which obliges them to a continuous improvement in the quality of services they offer to the society in education, investigation and culture.
In Spain ,as in the rest of the most developed countries, university education has experimented a deep transformation both in quantitative and in structural terms. Institutions such as traditional universities, which were thought in order to solve a limited demand, have had to solve a huge demand, becoming similar to the university education rates to primary education rates some decades ago. This increase means an important growth of the resources destined to its financing, which usually comes from public funds. Therefore, society has the right of hoping from the Universities some responsibility and efficacy in the management of these funds.
On the other hand, the existence of community programs as Erasmus, Comett and Lingua has meant the development of the interuniversity cooperation and the mobility of the students. So, instruments of evaluation are necessary to make the recognition of credits and degrees among different universities easier.
The goal of this paper is to build up a dynamic system model in order to be able to evaluate the quality of University of Valladolid. The paper is based on our own knowledge, conversations with a great number of experts and a document approved on the 25th of September, 1995, by the Council of Universities in the University of Almería: Programa de Evaluación Institucional de la Calidad de las Universidades.
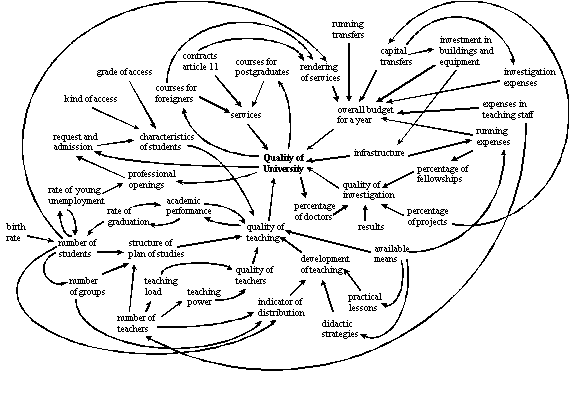
QUALITY OF UNIVERSITY
The evaluation of the quality in a university is related, in an integral way, to all relevant activities performed in the educational and investigation ambit as well as in the management of university services. In the same way, the organisation of formation courses or another cultural events are important in this sense. The progress in infrastructure and the overall budget for a year growth are also considered in order to evaluate the quality of university .
A bachelor's degree is evaluated in the teaching ambit, while a department is the unit to be evaluated in the investigation ambit. A correct structure in the plan of studies, a good development of teaching and the possibility of having the use of the adequate means contribute to an improvement in the quality of teaching. The human element is essential in order to evaluate the quality of teaching. Some appropriate characteristics of the registered students as well as of the teaching staff are factors to grow the quality of teaching. Nowadays, the existence of "clause numbers" in the most of bachelor's degrees is the cause why a lot of students do not study their desired bachelor's degree but the allowed ones by their grade of access, with the lack of motivation which this engenders. In order to evaluate the teaching staff, we consider its load and power teaching. The first one is the number of assigned hours to each teacher and the second one is the hours depending on the kind of teacher.
The rate of graduation is defined as the quotient of the number of graduates who finish in the theoretical time by the number of students matriculated in the first course the first time. This is an indicator of the level of academic performance and therefore of the quality of teaching. A combined evaluation of matriculated-presented-passed students has been made with the valuation of academic performance.
A growth in the quality of teaching causes an increasing in the professional openings for the students having a degree, which produces a growth in the requests of admission. The growth in the rate of young unemployment increases the number of students. There are two reasons in principle. On the one hand the alternative is "to stay at home doing nothing", and on the other hand it is common to think about whether finding work is easier with an university degree. The decrease of the birth rate in Spain happens to be an alarming element although its effect has not yet been appreciable in the university.
The variables considered to evaluate the quality of investigation in a department are the percentage of doctors over the total number of teachers, the percentage of projects and of fellowships of investigation conceded over the total solicited number and the obtained results: patents, thesis, articles, publications, ...
Among the financial variables that form the overall budget for a year, we have pointed out the most significant items, as our point of view, in the study of the quality of university. Entries by rendering of services increase with the registration fees, the courses for foreigners and the "contracts article 11". These last contracts are methods of the University of Valladolid which permits the Departments, the University Institutes and its teaching staff through themselves, to sign a contract with public or private concerns, or with a legal entity, for the realisation of works with a scientific, technological or artistic nature as well as the development of courses of specialisation. The running transfers are the main source of entries of public university. They proceed from subventions of public and private institution and they are basically dedicated to expenses in teaching staff and running expenses. The capital transfers increase with the entries generated by the conceded projects of investigation. They are destined to finance the investments in buildings and equipment and the expenses in investigation.
The increase in expenses and entries causes an increasing of the overall budget for a year. Among these, we have considered the running expenses which include the derived ones from daily functioning, maintenance and conservation of the installations, rents,… They are destined to cover the fellowships too, so an increasing of this item causes an increasing of the number of fellowships which promotes the formation of investigating staff and contributes to improve the researching quality in the departments.
In the causal diagram it is possible to see a great number of feedback loops, which to give an idea about the complexity in the study of the system.
REFERENCES
Comunidades Europeas - Comisión. 1993. Gestión de Calidad y Garantía de Calidad en la Enseñanza Superior Europea: Métodos y Mecanismos. Luxemburgo: Oficina de Publicaciones Oficiales de las Comunidades Europeas.
Consejo de Universidades. Secretaría General. 1995. Programa de Evaluación Institucional de la Calidad de las Universidades. Centro de Publicaciones. Secretaría General Técnica.
Sizer, J., Spee A., Bormans R. 1992. The rôle of performance
indicators in higher education. Higher Education 24: 133-155.
