Abstract: "Stock Broker Trading"
is an Interactive Learning Environment (ILE) that reflects the
basic dynamic of the stock market. Its main goal is to introduce
participants to their first experience as portfolio managers in
a dynamic and safe environment. Participants can feel how their
own individual decision interacts with other exogenous factors
in variable situations that affect their portfolio net worth in
an unpredictable way. The users of this ILE will understand the
behavior of the share price due to market forces; moreover, they
will experience a first approach of decision process to balance
capital performance and risk managing. This ILE is set on a network
that allows each user to observe how his actions, or lack of them,
in conjunction with those of the other users produce a fluctuation
on the share prices. Since each participant has a personal appreciation
of the facts as well as expectation for the future, and - in time
- different financial position, he will make different decisions
for his own strategy in reference to risk, safety or good performance.
This interaction of decisions will feedback the system creating
a dynamic behavior of its own. The learning experience is supported
by the debriefing process, where it will be possible to analyze
each decision and its consequences through the behavior of the
system.
Introduction
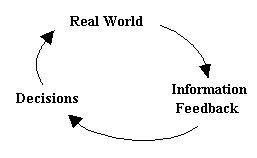
Over these last years, the financial sector has grown aware of the dynamic complexity of their own organization and their operating environment as well. Today, it is necessary to provide sophisticated tools for financial investors offering them the possibility to experimentally design and test policies. In this way, investors can form alternative investment strategies before they actually take action. The complexity of the financial sector depends on the underlying system structure which is characterized by delays, side effects, feedbacks, non-linearity, and vagueness. The generation of many problematic behaviors such as the unstable pattern of stock market price, arises from structure of its system. Most importantly, there is a strong relationship among structure, behavior, and external factors ( i.e. investors' decisions ) that can influence and shift the relative dominance of the structural components over time. By making decisions that alter the real system (Fig.1), investors receive information feedback about the real system, and using the new information, they revise their understanding of the system ( Sterman 1994 ). Unfortunately, there

| are some barriers to individual and organizational learning that are associated with the temporal and spatial boundaries of our mental models. To overcome such impediments, Sterman ( ibid. ) lists the benefits of simulation-based interactive learning environments in the form of "microworlds". |
"Stock Broker Trading" is an Interactive Learning Environment
(ILE) that reflects the basic dynamics of the stock market. Its
main goal is to introduce participants to their first experience
as portfolio managers in a dynamic and safe environment. The users
of this ILE will understand the behavior of the share price due
to market forces; moreover, they will experience a decision process
to balance capital performance and risk managing. This ILE is
set on a network that allows each user to observe how his actions,
or lack of them, in conjunction with those of the other users
produce a fluctuation on the share prices. The learning experience
is supported by both the debriefing process, where it will be
possible to analyze each decision and its consequences and the
ILE instructional design itself, which uses external stimuli to
initiate, assist, and support the internal processes of learning
( Gagné 1985 ).
The Stock Broker Trading
The design:
The SDBILE is a multi/single user network simulation game realized using Powersim® 2.5 software. Up to 4 players may participate in the simulation at the same time. In addition, a simulated player and a facilitator have been connected to the game. All players (investors) are competitors acting in the same system (market) where they give the same kind of input and receive the same kind of output (symmetric game). For this reason, the same user interface has been used for all players. In the simulation, the users of the game cyclically enter a planning phase, followed by an operational phase. When all users have made their decisions at a given point in time, the simulators automatically start running until the time for the next decision (operational mode). The player and facilitator interfaces (main models) are different and they share the same simulation model (co-model).
Player, facilitator and simulated player roles:
Player's role: He is a trainee financial manager selected for evaluation for promotion. An investment in a company is assigned to him with the instruction to trade shares for the best performance yield in one year period (time horizon). His Boss, the CFO, has selected from the corporate financial investment portfolio, a corporation which has some expected dividends, and has given him the responsibility of the administration of certain number of shares. He makes decisions on this investment once a week (time period). Every decision to buy or sell shares will cost a certain percentage of the operation as broker commission. Knowing that he will need some capital in order to trade with these shares, his boss assigns him some cash and, in addition, he can borrow money from the bank by paying interest. The bank will loan him money taking the shares that he owns as collateral at their current market price. The cash that he has deposited in the bank, will guarantee some monthly positive interest. After one year the CFO will examine his performance comparing it against the alternative investment.
Facilitator's role : The facilitator installs the game and may specify additional initializations (which will involve different scenarios). During the game, the Facilitator will act as an observer figuring out all important information for each player along all time horizon. He can also observe decisions taken by each player step by step. At the end of the game, he conducts the debriefing process, where it will be possible to analyze each decision and its consequences.
Simulated Player : It has been modeled so that
a decision making process leads the computer to act as a decision
maker in the game. Simulated decisions also allow us to test the
game by simulating one player against the computer.
Instructional Design
One of the most important guides in building this SDBILE has been the strong relationship between the external instructional events and the learning process. " In speaking of the event called learning, one often uses the phrase " the learning process ". Actually, according to modern research and theory, learning involves a whole set of internal processes, not just a single one. These processes are themselves unconscious and automatic. But they can be aided by some added external stimulation. These external stimuli serve to initiate, assist, and support the internal processes of learning. In whatever form, these external stimuli, systematically arranged, constitute what is called instruction " (Gagné ibid.). The following paragraphs contain brief descriptions about some of the relationship between the Gagné's processes of learning and their associated events of instruction within this SDBILE.
[Semantic encoding - Providing learning guidance] : Semantic encoding means putting incoming material in a form with such syntax that is thus made meaningful. In this SDBILE, this instruction has been defined showing causal loop diagrams, stock and flow diagrams, sub-system diagram and their associated explanation through the use of multimedia objects (sounds).
[Long term storage - Elaborate amount to be learned] : To add strength to what is stored in memory, DDE (Dynamic Data Exchange) links between Powersim® and Excel applications have been used to collect, elaborate, and analyze data generated by simulation. Moreover, a familiar interface for the players has been built in Excel by using Macro Language. Navigation buttons in both environments ( Excel and Powersim® ) allow to go back and forth for having different kind of information.
[Gratifying - Providing feedback about performance correctness] :
" What you measure is what you get " ; In this
SDBILE, a performance indicator has been introduced to support
the facilitator's role for giving positive or negative feedback
according to user's performance.
Future enhancements
References
Davidsen P.I. (1993) System Dynamics as a Platform for Educational Software Production. Barta et al. 1993, eds. 27-40.
Davidsen P.I. Implementing Elements of a System Dynamics Approach to Organizational Learning.
Forrester, Jay W. (1961). Industrial Dynamics. Productivity Press. Cambridge, MA.
Gagné R.M. (1995). Learning Processes and Instruction. Training Research Journal, Vol.1, pages 17-28.
Senge P.M. (1990). The Fifth Discipline. Doubleday Currency, N.Y.
Sterman J.D. (1994). Learning in and about complex systems. System Dynamics Review Vol. 10.